ARINC-429 vs MIL-STD-1553: this paper explores the similarities and differences between ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553, two widely used protocols in aviation data communication. ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553 serve as essential standards for reliable and efficient data transfer in aerospace applications. By analyzing their characteristics, features, and applications, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of both protocols, aiding decision-making processes for system designers and engineers in the aviation industry.
Introduction
The aviation industry relies on efficient and secure data communication protocols to ensure safe and reliable operations. ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553 are two prominent protocols utilized in avionics systems for transmitting data between avionics equipment. Understanding the similarities and differences between these protocols is crucial for selecting the appropriate one for specific aerospace applications.
Overview of ARINC-429
ARINC-429, established by the Aeronautical Radio Incorporated (ARINC), is a widely used protocol in commercial aviation. It operates on a unidirectional, point-to-point architecture and supports data rates up to 100 kbps. ARINC-429 utilizes a differential voltage interface and supports a maximum of 20 receivers per transmitter.
Overview of MIL-STD-1553
MIL-STD-1553, developed by the United States Department of Defense, is a robust and time-tested protocol commonly employed in military and aerospace applications. It operates on a dual-redundant, balanced, and differential serial bus architecture. MIL-STD-1553 supports data rates up to 1 Mbps and allows for up to 31 remote terminals.
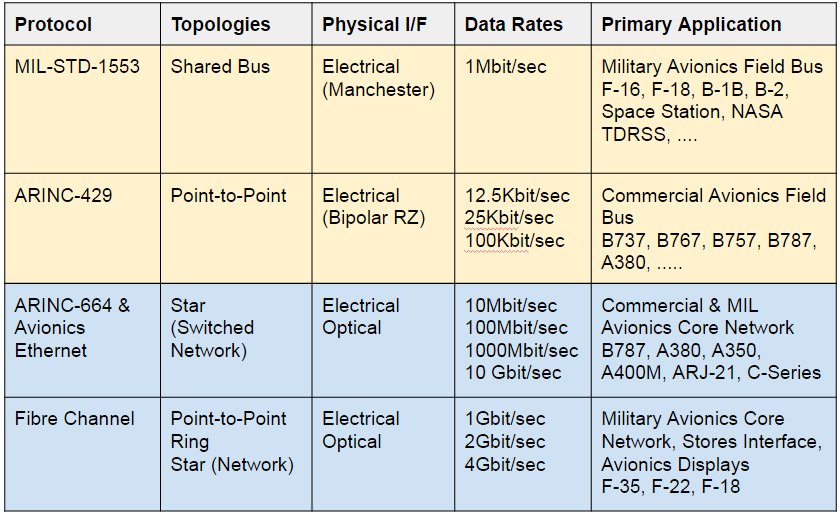
Comparison of Characteristics
4.1 Data Transfer: Both ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553 use serial transmission for data transfer, but they differ in terms of bit encoding. ARINC-429 employs bi-phase modulation, while MIL-STD-1553 uses Manchester encoding. MIL-STD-1553 also provides built-in error checking mechanisms for enhanced data integrity.
4.2 Bus Architecture: ARINC-429 uses a point-to-point architecture, limiting it to a single transmitter and multiple receivers. In contrast, MIL-STD-1553 employs a bus architecture with multiple remote terminals, allowing for distributed communication and improved fault tolerance.
4.3 Data Rate: ARINC-429 supports data rates up to 100 kbps, making it suitable for low to moderate data transfer requirements. MIL-STD-1553 offers higher data rates up to 1 Mbps, enabling faster and more extensive data transmission.
4.4 Redundancy: While ARINC-429 does not inherently provide redundancy, it can be implemented using external devices. MIL-STD-1553 incorporates built-in redundancy through dual-redundant data buses and remote terminal operation, ensuring system reliability in critical applications.
Applications
ARINC-429 is predominantly used in commercial aviation for various purposes, including flight control systems, engine monitoring, and weather radar. Its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and wide industry adoption make it a popular choice in commercial aircraft.
MIL-STD-1553 finds extensive application in military and aerospace systems where robustness, fault tolerance, and high data transfer rates are crucial. It is commonly utilized in aircraft avionics, weapon systems, and missile guidance.
Conclusion
ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553 are essential protocols in aviation data communication, each with its own strengths and areas of application. ARINC-429 is well-suited for commercial aviation due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while MIL-STD-1553 excels in military and aerospace systems where high data rates and fault tolerance are critical. The selection of the appropriate protocol depends on the specific requirements of the system and the application.
Understanding the similarities and differences between ARINC-429 and MIL-STD-1553 is vital for avionics engineers and system designers. By considering factors such as data transfer characteristics, bus architecture, data rates, and redundancy, engineers can make informed decisions in choosing the most suitable protocol for their aviation applications.
References:
ARINC-429: Avionics Digital Information Bus, ARINC Specification 429, Aeronautical Radio Incorporated (ARINC), 2018.
MIL-STD-1553B: Notice 2, Department of Defense Interface Standard, Aircraft Internal Time Division Command/Response Multiplex Data Bus, 2007.
Hejkal, V. & Rončević, N. (2018). Comparative Analysis of ARINC 429 and MIL-STD-1553B Protocols for Space Applications. IEEE Access, 6, 4005-4017.
Thomerson, T. L. (2014). ARINC 429: An Avionics Data Bus. NASA/TM—2014-218940.
Johnson, J. (2015). MIL-STD-1553: How it Works and Its Advantages in Aerospace Applications. Data Device Corporation.





