Decoding ARINC-429 Labels: This paper provides a comprehensive beginner’s guide to decoding ARINC-429 labels, enabling accurate interpretation of data in avionics systems. The paper explores the structure and significance of ARINC-429 labels, discusses label formats, and provides examples of commonly used labels. By understanding the intricacies of ARINC-429 labels, avionics professionals can effectively interpret data and enhance their understanding of avionics communication.
- Introduction
ARINC-429 labels play a crucial role in avionics communication, providing vital information about the data being transmitted. This paper serves as a beginner’s guide to decoding ARINC-429 labels, helping avionics professionals accurately interpret data and gain insights into avionics systems and protocol converters.
- Understanding ARINC-429 Labels
ARINC-429 labels are numeric identifiers assigned to specific data parameters or system functions. These labels act as descriptors, enabling avionics systems to identify the nature and purpose of the transmitted data. Labels are an essential component in ARINC-429 communication, facilitating proper data interpretation.
- Label Formats
ARINC-429 labels can be categorized into two formats: standard labels and reserved labels. Standard labels are used for general data parameters, while reserved labels are assigned for specific system functions or purposes. Standard labels range from 0 to 2047, while reserved labels range from 2048 to 4095.
- Label Structure
ARINC-429 labels consist of two fields: the Source/Destination Identifier (SDI) field and the Equipment Identifier (EI) field. The SDI field represents the source or destination of the data, while the EI field identifies the specific data parameter or system function associated with the label.
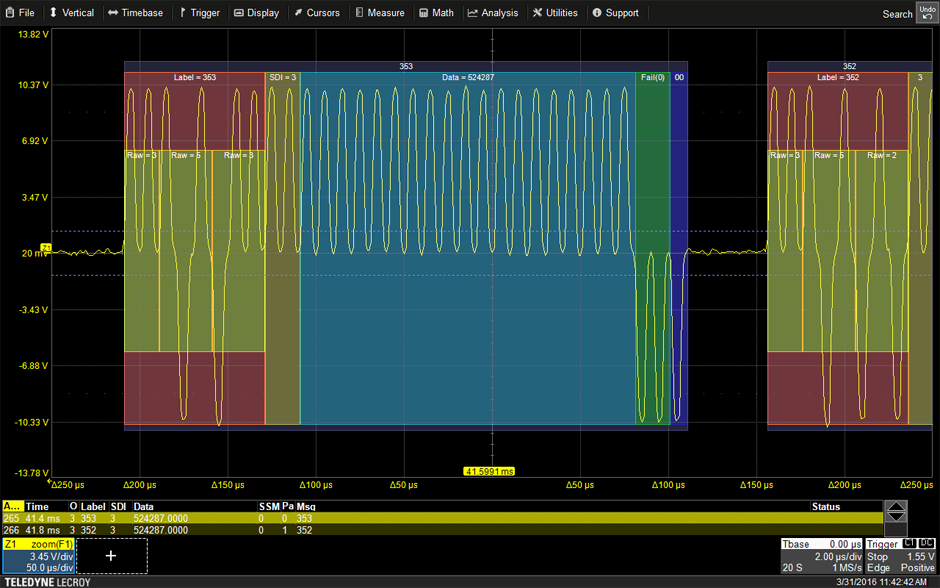
- Examples of Commonly Used Labels
Label 101: Altitude
Label 71: Aircraft Speed
Label 235: Flight Management System Navigation Data
Label 310: Engine Data
Label 520: Weather Radar Data
These examples illustrate the wide range of data parameters that can be conveyed through ARINC-429 labels. Avionics professionals should become familiar with commonly used labels in their specific areas of expertise to accurately interpret data in avionics systems.
- Interpretation and Data Analysis
Decoding ARINC-429 labels is crucial for accurate data interpretation and analysis in avionics systems. By understanding the assigned labels, avionics professionals can extract meaningful information from the transmitted data and make informed decisions based on the data analysis.
- Label Databases and Specifications
To facilitate the interpretation of ARINC-429 labels, several databases and specifications are available, providing comprehensive information on label assignments, associated data parameters, and system functions. These resources serve as valuable references for avionics professionals seeking to decode ARINC-429 labels accurately.
- Conclusion
Decoding ARINC-429 labels is essential for accurately interpreting data in avionics systems. By understanding the structure, formats, and significance of labels, avionics professionals can extract meaningful information and gain insights into avionics communication. Familiarity with commonly used labels and utilizing label databases and specifications will enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of data analysis in avionics systems.
64f7c700-33fe-4145-9274-8991950ffd18
References:
ARINC Specification 429-18: Mark 33 Digital Information Transfer System (DITS), Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC), 2001.
ARINC Specification 429-19: Mark 33 Digital Information Transfer System (DITS), Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC), 2003.
ARINC Report 419-6: Guidance for the Design of an ARINC 429 Data Bus Network, Aeronautical Radio, Inc. (ARINC), 2012.
The ARINC 429 Protocol Tutorial, Ballard Technology, Inc., 2019.
ARINC 429 Label Database, Rockwell Collins, Inc.
ARINC 429 Label Database, Collins Aerospace, 2020.
B. Cooke, “Avionics Data Bus Tutorial – Part 3: ARINC 429,” EE Times, 2012.





