Comprehensive Guide to MIL-STD-461 Testing. Learn the key aspects and best practices of MIL-STD-461 testing to ensure compliance and electromagnetic compatibility in military equipment. This white paper provides a comprehensive guide to MIL-STD-461 testing, outlining its significance, testing procedures, and essential considerations for military contractors and suppliers.
Introduction
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is crucial for the reliable and effective operation of military equipment. To address the challenges posed by electromagnetic interference, the United States Department of Defense (DoD) developed MIL-STD-461. This standard defines the testing requirements and procedures necessary to ensure military equipment’s compliance with electromagnetic compatibility guidelines. This white paper serves as a comprehensive guide to MIL-STD-461 testing, protocol converters, providing insights into its importance, testing methodologies, and best practices to achieve electromagnetic compatibility in military systems.
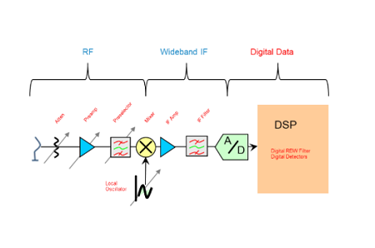
The Significance of MIL-STD-461 Testing
MIL-STD-461 testing is vital for the successful deployment of military equipment in various operational environments. It ensures that electronic systems can function cohesively without disrupting one another while operating in the presence of electromagnetic interference. Compliance with MIL-STD-461 safeguards mission-critical systems from unexpected failures, minimizes electromagnetic interference with civilian devices, and reduces the risk of detection during electronic warfare scenarios.
Key Aspects of MIL-STD-461 Testing
- Testing Applicability: MIL-STD-461 testing applies to all electronic equipment, subsystems, and systems that are intended for use in military applications. It is essential for manufacturers, contractors, and suppliers to understand the scope of equipment covered by the standard.
- Testing Requirements: The standard outlines specific test levels and procedures that equipment must undergo to evaluate its electromagnetic emissions and susceptibility characteristics. These requirements ensure consistency and uniformity in testing across different platforms and manufacturers.
- Conducted Emissions Test (CE): This test assesses the electromagnetic emissions conducted through power and signal cables. It evaluates the equipment’s ability to limit unwanted emissions to acceptable levels.
- Radiated Emissions Test (RE): This test measures the electromagnetic emissions radiated by the equipment when it is in operation. It ensures that the equipment does not emit excessive electromagnetic radiation that could interfere with other systems.
- Conducted Susceptibility Test (CS): This test evaluates the equipment’s capability to withstand conducted interference from external sources, such as power surges or radio frequency signals.
- Radiated Susceptibility Test (RS): This test assesses the equipment’s resilience against radiated electromagnetic interference from external sources, simulating real-world scenarios.
MIL-STD-461 Testing Best Practices
- Early Design Considerations: Incorporating EMC design considerations early in the development process helps mitigate potential issues and reduces the need for costly redesigns later on.
- Modular Testing: Breaking down complex systems into modular components allows for targeted testing, identifying specific sources of interference and simplifying the troubleshooting process.
- Testing throughout Development: Conducting testing at various stages of development ensures that potential EMC issues are identified and resolved promptly, avoiding costly delays in the final stages.
- Certified Testing Facilities: Employing accredited testing facilities ensures accurate and reliable results, as they adhere to strict quality standards.
- Documentation and Recordkeeping: Thorough documentation of the testing process, test results, and any design modifications is crucial for compliance verification and future reference.
Challenges and Solutions
- Multi-Domain Operations: Military systems today operate across various domains, such as land, sea, air, and cyberspace. Testing MIL-STD-461 compliance across these domains requires a comprehensive approach, addressing potential interoperability challenges.
- Miniaturization and Integration: As military equipment becomes smaller and more integrated, controlling electromagnetic emissions becomes increasingly challenging. Implementing proper shielding and grounding techniques is essential to address these issues.
- Emerging Technologies: New technologies, such as artificial intelligence, advanced communication systems, and unmanned systems, pose unique EMC challenges. Continuous research and testing are necessary to adapt MIL-STD-461 to accommodate these innovations.
Conclusion
MIL-STD-461 testing is indispensable for ensuring the electromagnetic compatibility and reliable operation of military equipment. By following best practices and understanding the key aspects of testing, military contractors and suppliers can achieve compliance and contribute to the success of modern military operations. Striving for EMC in military systems not only protects against disruption and interference but also enhances operational effectiveness and safety for military personnel.
References:
United States Department of Defense. “MIL-STD-461G: Requirements for the Control of Electromagnetic Interference Characteristics of Subsystems and Equipment.” Washington, DC: U.S. Government Publishing Office, 2015.
Buehler, Martin G. “Electromagnetic Compatibility Engineering.” Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2009.
Carpenter, Mark. “Electromagnetic Compatibility: Principles and Applications.” Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2017.
Dobmann, Gregory. “Electromagnetic Compatibility in Power Electronics.” New York, NY: Springer, 2016.
U.S. Army Research Laboratory. “Electromagnetic Compatibility Design Guide for Tactical Radio Systems.” Technical Report ARL-TR-6725, 2014.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). “IEC 61000-4-2: Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) – Part 4-2: Testing and Measurement Techniques – Electrostatic Discharge Immunity Test.” Geneva, Switzerland: IEC, 2008.
NATO Standardization Agency (NSA). “STANAG 7173: EMC for Systems.” Brussels, Belgium: NATO Standardization Agency, 2012.
IEEE Electromagnetic Compatibility Society. “IEEE Standard for Electromagnetic Compatibility – Requirements and Tests.” IEEE Std 149-2001, 2001.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC). “Title 47: Telecommunication, Part 15 – Radio Frequency Devices.” Code of Federal Regulations, Washington, DC: U.S. Government Publishing Office.
United States Department of Defense. “MIL-STD-464C: Electromagnetic Environmental Effects Requirements for Systems.” Washington, DC: U.S. Government Publishing Office, 2010.





