This white paper provides a comprehensive comparison of the MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 data buses. MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 are both extensively used in the aerospace and defense industries for reliable data communication. By understanding the similarities and differences between these protocols, engineers and professionals can make informed decisions regarding the selection and implementation of data bus systems in their applications.
Introduction
The MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 data buses are widely used in the aerospace and defense industries. This section introduces the two protocols and highlights their significance in facilitating data communication in critical applications.
Architecture and Physical Layer
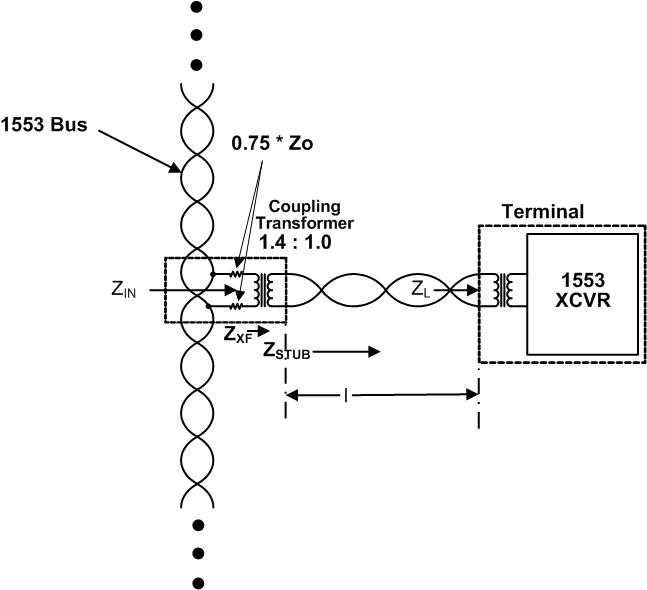
MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 employ different architectural approaches and physical layer specifications. This section discusses the dual-bus architecture of MIL-STD-1553, consisting of a data bus and a command/status bus, while ARINC 429 uses a point-to-point configuration. Additionally, the physical layer characteristics, such as voltage levels and cable types, are compared.
Data Transmission and Message Structure
The data transmission methods and message structures of MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 differ significantly. MIL-STD-1553 utilizes time-division multiplexing and fixed-length words, while ARINC 429 uses a variable-length message structure. This section explores the implications of these differences on data transmission efficiency and flexibility.
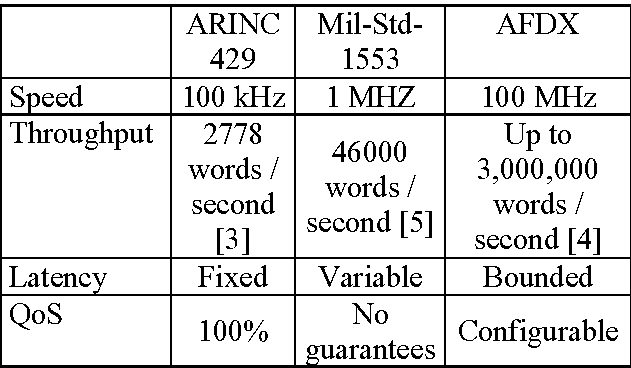
Data Rate and Throughput
MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 have different data rates and throughput capabilities. This section compares the maximum data rates supported by each protocol and discusses their impact on system performance and real-time data exchange.
Application and Industry Adoption
MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 have found widespread adoption in various applications within the aerospace and defense industries. This section explores their respective applications, highlighting the strengths and limitations of each protocol in specific use cases.
Error Detection and Correction
Reliable data communication requires robust error detection and correction mechanisms. This section compares the error detection and correction capabilities of MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429. It discusses the use of parity bits, cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), and other error detection methods in both protocols.
System Integration and Compatibility
Integrating data bus systems with existing infrastructure and components is crucial. This section explores the compatibility of MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 with different hardware and software components. Considerations such as system scalability, interoperability, and the availability of compatible devices are discussed.
Design Considerations
When selecting a data bus protocol, several design considerations come into play. This section covers factors such as system complexity, cost, power consumption, and the availability of development tools and resources for MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this white paper provides a comprehensive comparison of the MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 data buses. By understanding the similarities and differences between these protocols, engineers and professionals can make informed decisions regarding the selection and implementation of data bus systems in their applications. Both protocols have proven their effectiveness in facilitating reliable data communication in the aerospace and defense industries, and their unique characteristics make them suitable for specific use cases and requirements.
By understanding the similarities and differences between MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429, engineers and professionals can make informed decisions regarding the selection and implementation of data bus systems in their applications. Both protocols have their unique strengths and are widely adopted in the aerospace and defense industries. MIL-STD-1553 excels in complex, mission-critical applications where deterministic communication and fault tolerance are essential. ARINC 429, on the other hand, is well-suited for applications requiring simplicity, low cost, and compatibility with legacy systems.
The comparison between MIL-STD-1553 and ARINC 429 in this white paper provides valuable insights into the capabilities, applications, and design considerations of these two widely used data bus protocols. By understanding the similarities and differences, professionals can effectively evaluate their requirements and select the most appropriate protocol for their specific needs. Whether it is the robustness and determinism of MIL-STD-1553 or the simplicity and compatibility of ARINC 429, both protocols play vital roles in enabling reliable data communication in the aerospace and defense industries.
References:
MIL-STD-1553 – Department of Defense Interface Standard, MIL-STD-1553, 2015.
ARINC Specification 429: Mark II, Digital Information Transfer System (DITS), 2018.
Bhaskar, K. V., & Katti, C. P. (2017). MIL-STD-1553B Bus Controller IP Core Implementation on FPGA. In 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS) (pp. 944-948). IEEE.
Jones, R. (2013). Avionics Navigation Systems. CRC Press.
Phillips, E. P. (2000). Avionics Training: Systems, Installation, and Troubleshooting. CRC Press.





